The Science of Nutrition: Foods That Nourish and Heal
Introduction
Nutrition is an ever-evolving field that encompasses the study of food and its relationship to health. At its core, nutrition explores how the nutrients in our diet influence our overall well-being, disease prevention, and even recovery. As we deepen our understanding of the biochemical interactions between food compounds and the human body, it becomes evident that certain foods not only nourish but can also support healing processes. This article will delve into the science of nutrition, exploring the foods that help us thrive and recover, supported by modern research and insights.
The Basics of Nutrition
Macronutrients and Micronutrients
Nutrition is primarily composed of macronutrients and micronutrients.
-
Macronutrients: These are nutrients that provide energy and are required in larger amounts. They include:
- Carbohydrates: The body’s main source of energy, found in foods like grains, fruits, and vegetables.
- Proteins: Essential for the repair and growth of tissues, proteins are found in meats, dairy, legumes, and nuts.
- Fats: Necessary for hormone production and absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, healthy fats can be found in fish, nuts, seeds, and oils.
- Micronutrients: These include vitamins and minerals required in smaller amounts but play crucial roles in numerous bodily functions. For instance:
- Vitamins: Organic compounds essential for metabolic processes, such as Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) for immune function and Vitamin D for calcium absorption.
- Minerals: Inorganic elements like calcium and iron, critical for bone health and oxygen transport in the blood.
The Role of Phytochemicals
Beyond macronutrients and micronutrients, many foods contain bioactive compounds known as phytochemicals. These are natural plant compounds that can influence health positively. Examples include:
- Flavonoids: Found in berries, tea, and grapes, these compounds may reduce inflammation and lower the risk of chronic diseases.
- Carotenoids: Present in carrots, sweet potatoes, and greens, these pigments are known for their antioxidant properties.
The science surrounding these compounds is ongoing, revealing their potential to offer therapeutic benefits and support wellness.
Foods That Nourish
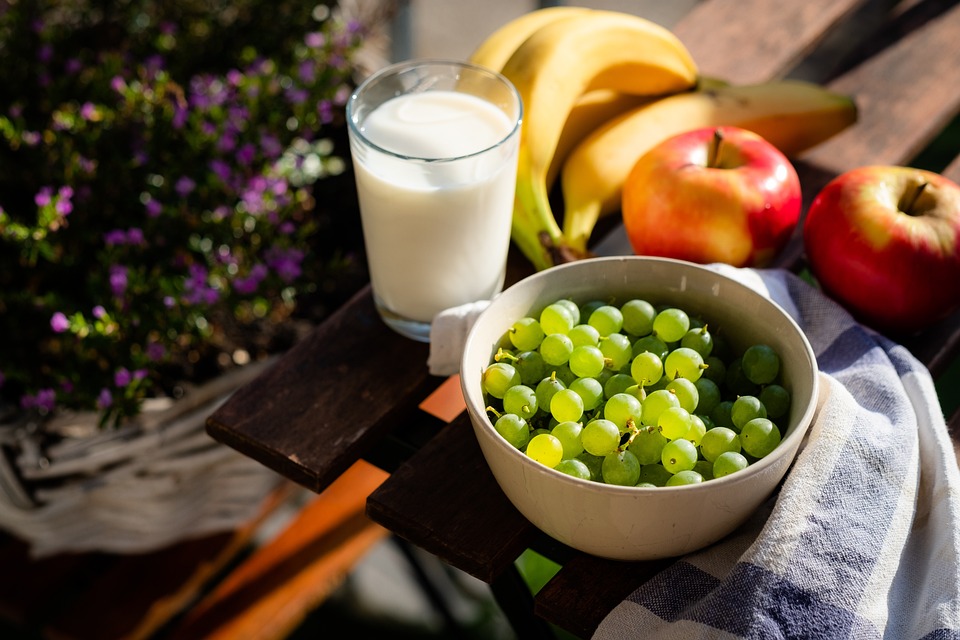
Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are cornerstones of a nutritious diet. They are rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber.
-
Leafy Greens: Spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are high in vitamins A, C, K, and several minerals, including calcium and potassium. They have been linked to reduced risk of heart disease and certain types of cancer due to their high antioxidant content.
- Berries: Blueberries, strawberries, and raspberries are particularly rich in vitamins and antioxidants. Studies indicate that regular consumption of berries may enhance cognitive function and lower blood pressure.
Whole Grains
Whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and oats are packed with fiber, which promotes digestive health and satiety.
- Fiber: A high intake of dietary fiber is associated with lower risks of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer. Whole grains also provide B vitamins and minerals such as iron and magnesium.
Healthy Fats
Sources of healthy fats, including avocados, nuts, and olive oil, are crucial for overall health.
-
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fish (like salmon and mackerel) and flaxseeds, these fatty acids support heart health and reduce inflammation.
- Monounsaturated Fats: These fats, prevalent in olive oil and avocados, are known to improve cholesterol levels and support heart health.
Lean Proteins
Lean proteins such as chicken, fish, legumes, and tofu provide essential amino acids necessary for tissue repair and immune function.
-
Fish: Regular consumption of fish, particularly fatty fish rich in omega-3s, has been linked to lower risks of cardiovascular disease and improved brain health.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent protein sources that also deliver fiber, iron, and other nutrients.
Foods That Heal
Healing Herbs and Spices
Herbs and spices not only enhance flavor but also offer medicinal properties.
-
Turmeric: Contains curcumin, a potent anti-inflammatory compound that may help in conditions like arthritis and may also possess anti-cancer properties.
- Ginger: Known for its anti-nausea effects, ginger has also been studied for its potential to reduce inflammation and improve digestive health.
Fermented Foods
Fermented foods like yogurt, kimchi, and sauerkraut support gut health by providing probiotics, live microorganisms that can confer health benefits.
- Gut Microbiome: A balanced gut microbiome is crucial for digestion, immune function, and even mental health. Regular consumption of fermented foods can enhance the diversity of gut bacteria, leading to improved health outcomes.
Bone Broth
Bone broth is gaining popularity as a nutrient-dense food that is beneficial for joint and gut health.
- Collagen: Rich in collagens, bone broth may support skin elasticity and joint health. The amino acids in bone broth, like glycine and proline, are vital for repairing tissues and reducing inflammation.
Superfoods
Superfoods are nutrient-rich foods considered to be especially beneficial for health and well-being.
-
Quinoa: A complete protein, quinoa contains all nine essential amino acids, making it an excellent choice for vegetarians and vegans.
- Chia Seeds: Loaded with omega-3s, fiber, and antioxidants, these tiny seeds can enhance heart health and improve digestion.
The Importance of Balanced Nutrition
A balanced diet should include a variety of foods to provide all necessary nutrients. The benefits of a well-rounded diet are supported by numerous studies indicating that whole, unprocessed foods can lead to better health outcomes.
The Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet, known for its emphasis on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, healthy fats, and lean proteins, has been extensively researched.
- Heart Health: Studies show that following this diet reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke. Its anti-inflammatory properties are particularly beneficial for overall well-being.
Plant-Based Diets
Plant-based diets emphasize whole plant foods while reducing or eliminating animal products. Research indicates that such diets can lead to lower risks of chronic diseases and promote longevity.
- Chronic Diseases: Plant-based eating patterns have been linked to reduced risks of obesity, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and certain cancers.
The Impact of Nutrition on Mental Health
Emerging research highlights the intricate relationship between nutrition and mental health.
Nutrient Deficiencies
Deficiencies in certain nutrients can influence mood and cognitive function.
-
Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Low levels have been associated with increased risks of depression and anxiety. Consuming fatty fish or flaxseeds may help mitigate these effects.
- B Vitamins: Vitamins like B6, B12, and folate play significant roles in neurotransmitter function. Deficiencies in these vitamins are linked to mental health disorders.
The Gut-Brain Connection
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication pathway between the gastrointestinal tract and the brain.
- Probiotics: Probiotics may improve mental well-being by modulating gut microbiota, thereby influencing mood and cognitive functions. Studies have indicated that maintaining a healthy gut flora can positively affect the brain.
Conclusion
Understanding the science of nutrition is essential in recognizing how food can nourish our bodies and facilitate healing. A diet rich in whole foods, combined with specific foods known for their healing properties, can significantly improve physical and mental health. As research continues to evolve, it becomes increasingly clear that nutrition is a fundamental pillar of health.
By making informed dietary choices, we have the power to nourish our bodies, support healing, and promote overall well-being. Engaging with nutrition science not only empowers us to make better food choices but also allows us to appreciate the profound relationship between diet and health.
References
This article is based on a synthesis of current research and literature in the field of nutrition. For specific references, please refer to academic journals, nutritional studies, and governmental health guidelines.

























Add Comment